Failing to meet industrial standards can lead to equipment failure and safety hazards. Discover how JP Gas Spring ensures full compliance with GB/T 25751-2010 for reliable performance.
Compression gas springs must adhere to GB/T 25751-2010 to guarantee parameters like force tolerance and corrosion resistance. JP Gas Spring specializes in standardized solutions for global industries.

Let’s examine three critical aspects of GB/T 25751-2010 compliance and how JP Gas Spring delivers optimized solutions.
What Critical Parameters Define Compression Gas Spring Performance?
Industrial equipment often fails due to misaligned gas spring parameters. Understanding GB/T 25751-2010 standards is essential to avoid costly downtime.
Key performance indicators include piston rod diameter, force tolerance, and cycle life—all specified in GB/T 25751-2010 to ensure consistent operation across applications.
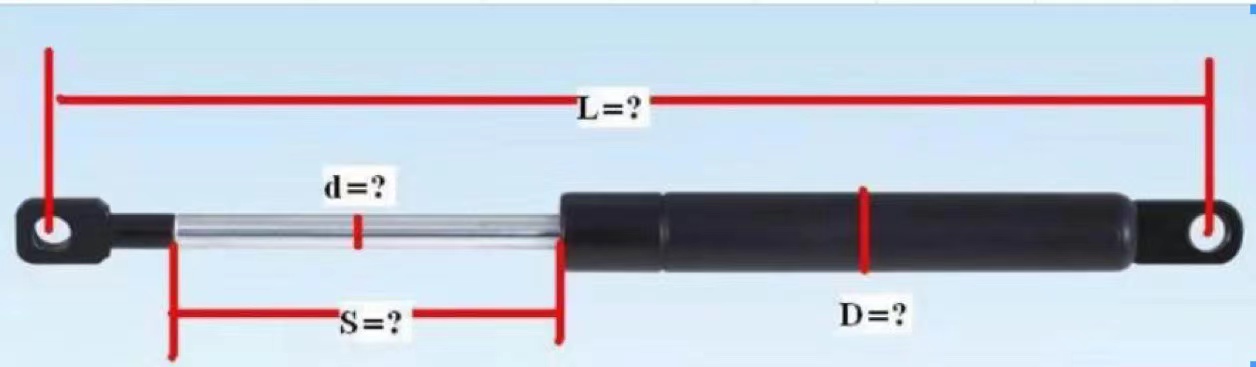
Technical Breakdown
1. Diameter Ratio & Tolerance
- Standard Requirement: Piston rod diameter (d) to cylinder inner diameter (D₁) ratio ≥1.1 (6.1.1)
2. Force Characteristics
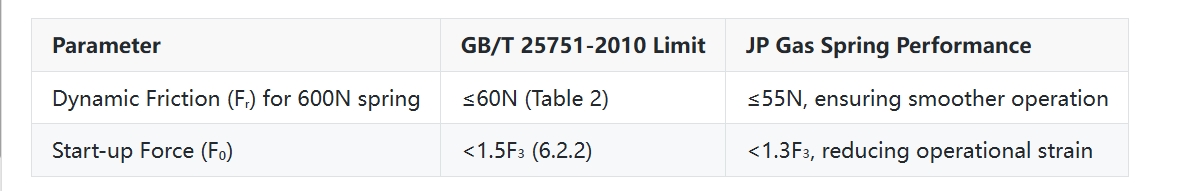
3. Cycle Life
- Standard Requirement: 25,000 cycles with ≤13% nominal force decay (6.5.1)
- JP Testing: 30,000 cycles validated, the force decay is controlled within 8%, outperforming industry norms.
Case Study: JP’s Solution for a US Packaging Manufacturer
A leading US packaging firm faced frequent equipment failures due to non-compliant gas springs. JP Gas Spring provided custom solutions:
- Challenge: Gas springs failed at 15,000 cycles, causing production halts.
- JP Solution: Implemented GB/T 25751-2010 compliant springs with 30,000-cycle life.
- Result: Downtime reduced by 65%, annual maintenance costs saved $42,000.
graph TD
A[US Packaging Firm] --> B[Cycle Life Failure]
B --> C[JP's GB/T 25751-2010 Springs]
C --> D[30,000 Cycles & 8% Decay]
D --> E[65% Downtime Reduction]How to Ensure Temperature Resistance in Compression Gas Springs?
Extreme temperatures can degrade gas spring performance, leading to equipment malfunction in harsh environments.
GB/T 25751-2010 specifies rigorous temperature cycling tests to ensure reliability. JP Gas Spring’s thermal validation process exceeds standard requirements for global applications.
Technical Breakdown
1. High/Low Temperature Protocol
- Standard Test: 110°C storage + -40°C~80°C 2 cycles, nominal force decay ≤5% (6.4)
- JP Enhancement: 120°C storage + -45°C~85°C 3 cycles, decay ≤3.5%, suitable for arctic and desert conditions.
2. Material Selection
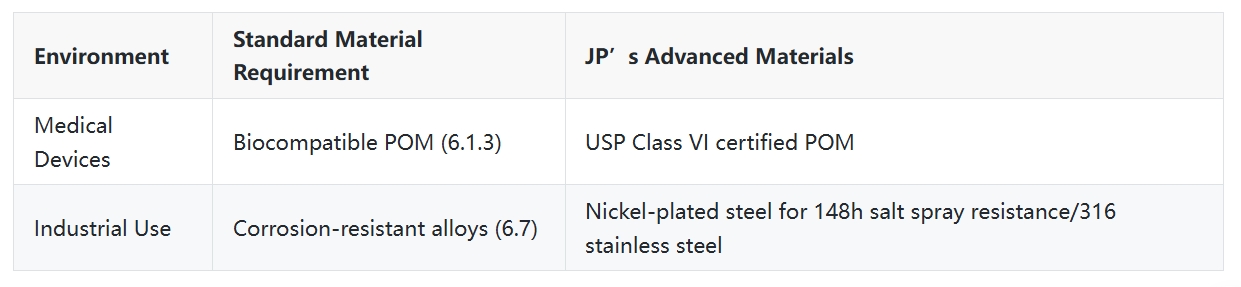
3. Thermal Cycling Impact
- Non-compliant Risk: Force decay >15% in extreme temperatures, causing sudden equipment failure.
- JP’s Solution: Proprietary oil formulations maintain viscosity across -25°C~65°C, ensuring consistent performance.
Case Study: JP’s Desert-Ready Solution for an Indian Mining Company
An Indian mining operation needed gas springs for equipment operating in 50°C+ temperatures:
- Challenge: Existing springs failed within 3 months due to thermal decay.
- JP Solution: Deployed GB/T 25751-2010 springs with UV-resistant seals and high-temperature oil.
- Result: 0 failures in 18 months, maintenance costs reduced by 70%.
graph TD
A[Indian Mining] --> B[50°C+ Operation]
B --> C[JP's High-Temp Springs]
C --> D[UV Seals & High-Temp Oil]
D --> E[18 Months Zero Failures]How to Achieve Corrosion Resistance in Compression Gas Springs?
Corrosion compromises gas spring integrity, especially in coastal or chemical-intensive environments.
GB/T 25751-2010 sets strict corrosion resistance standards. JP Gas Spring’s multi-layer coating systems exceed these requirements for prolonged service life.
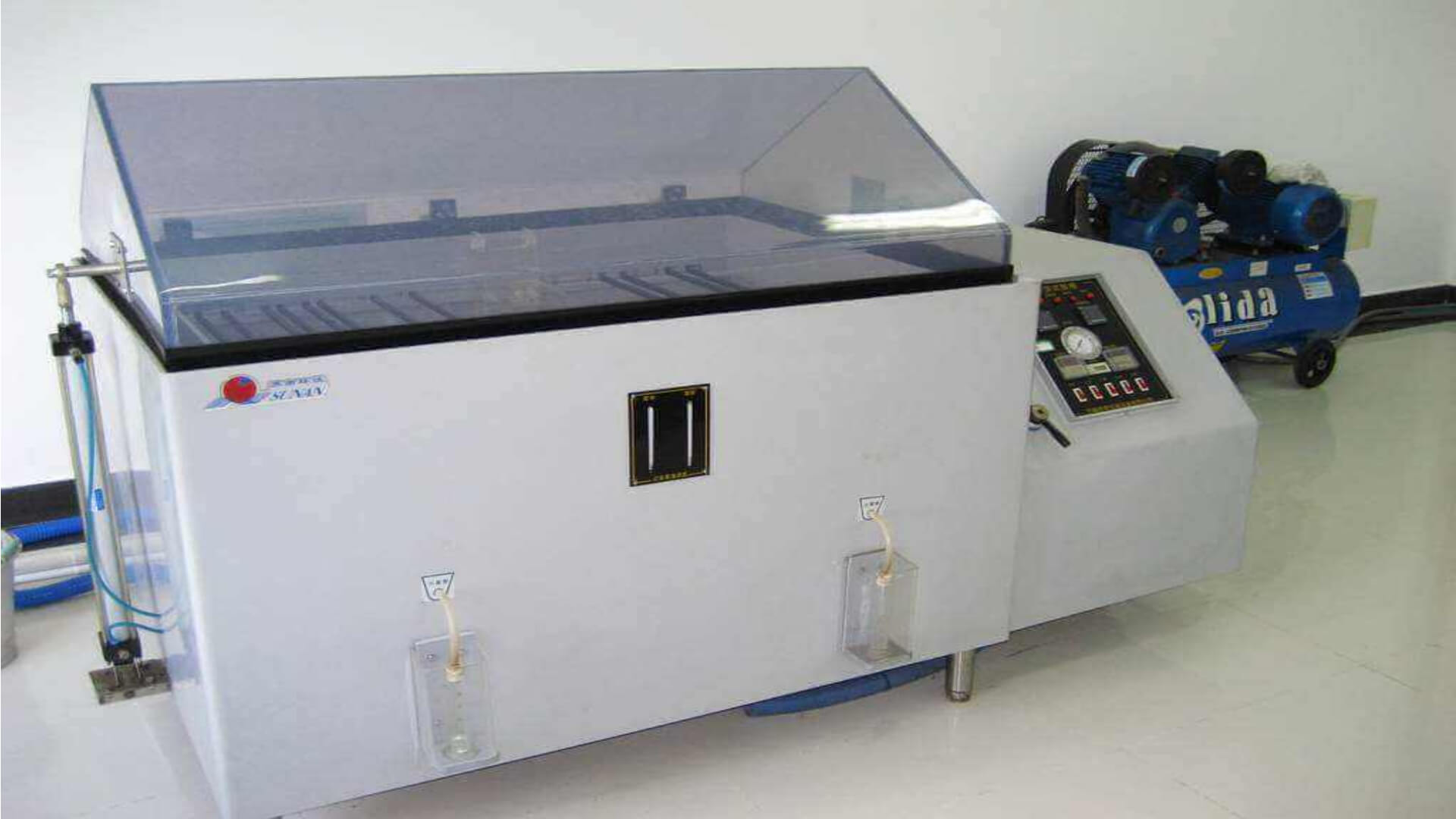

Technical Breakdown
1. Salt Spray Testing
- Standard Requirement: 96h neutral salt spray without blistering (6.7.1)
- JP Performance: Max 360h salt spray test passed.
2. Coating Systems
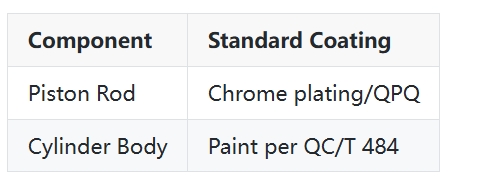
3. Environmental Applications
- Marine Use: JP’s stainless steel springs with PTFE coatings withstand saltwater exposure.
- Chemical Plants: Hastelloy alloys resist corrosion from acids and alkalis, exceeding standard material limits.
Case Study: JP’s Coastal Solution for a Mexican Seaport
A Mexican seaport required gas springs for container handling equipment:
- Challenge: Seawater corrosion caused frequent replacements every 6 months.
- JP Solution: Supplied GB/T 25751-2010 springs with duplex stainless steel and PTFE seals.
- Result: Service life extended to 5 years, replacement costs reduced by 80%.
graph TD
A[Mexican Seaport] --> B[Seawater Corrosion]
B --> C[JP's Duplex Steel Springs]
C --> D[PTFE Seals & Triple Coating]
D --> E[5-Year Service Life]Ready to Implement GB/T 25751-2010 Compliant Gas Springs?
JP Gas Spring ensures full compliance with GB/T 25751-2010, delivering reliable performance across industries.
- Share Your Requirements: Email specs to info@jpgasspring.com
- Receive Custom Solutions: Get GB/T 25751-2010 compliant recommendations within 12h
- Test Prototypes: Validate performance with free samples (MOQ 100pcs)
Global Support:
- India/Mexico/US: Local sales engineers for on-site support
- 6 Continents: Over 300 clients trust JP’s standardized solutions
Download Technical Catalog: https://jpgasspring.com/catalog/
Contact Us: info@jpgasspring.com